Bitcoin’s fourth halving launched a long-term and a short-term shift in miner income composition because it decreased the quantity of BTC rewarded to miners for every mined block by 50% — immediately impacting miner incentives and, by extension, the broader Bitcoin economic system.
On April 19, simply earlier than the halving, transaction charges constituted 11% of whole miner income, a determine that has been comparatively secure all year long. Nevertheless, the halving occasion on April 20 precipitated a considerable change, with transaction charges skyrocketing to over 75% of miner income.
The surge in charges could be attributed to a mix of things. Firstly, a major a part of the market may need raced to settle their transactions earlier than the halving, which has pushed up transaction charges.
Secondly, there gave the impression to be a rising demand for transactions, and customers wished to be included within the halving block itself. Most of this demand may very well be attributed to Ordinals, as inscriptions on the coveted block 840,000 may very well be value extra on the secondary market.
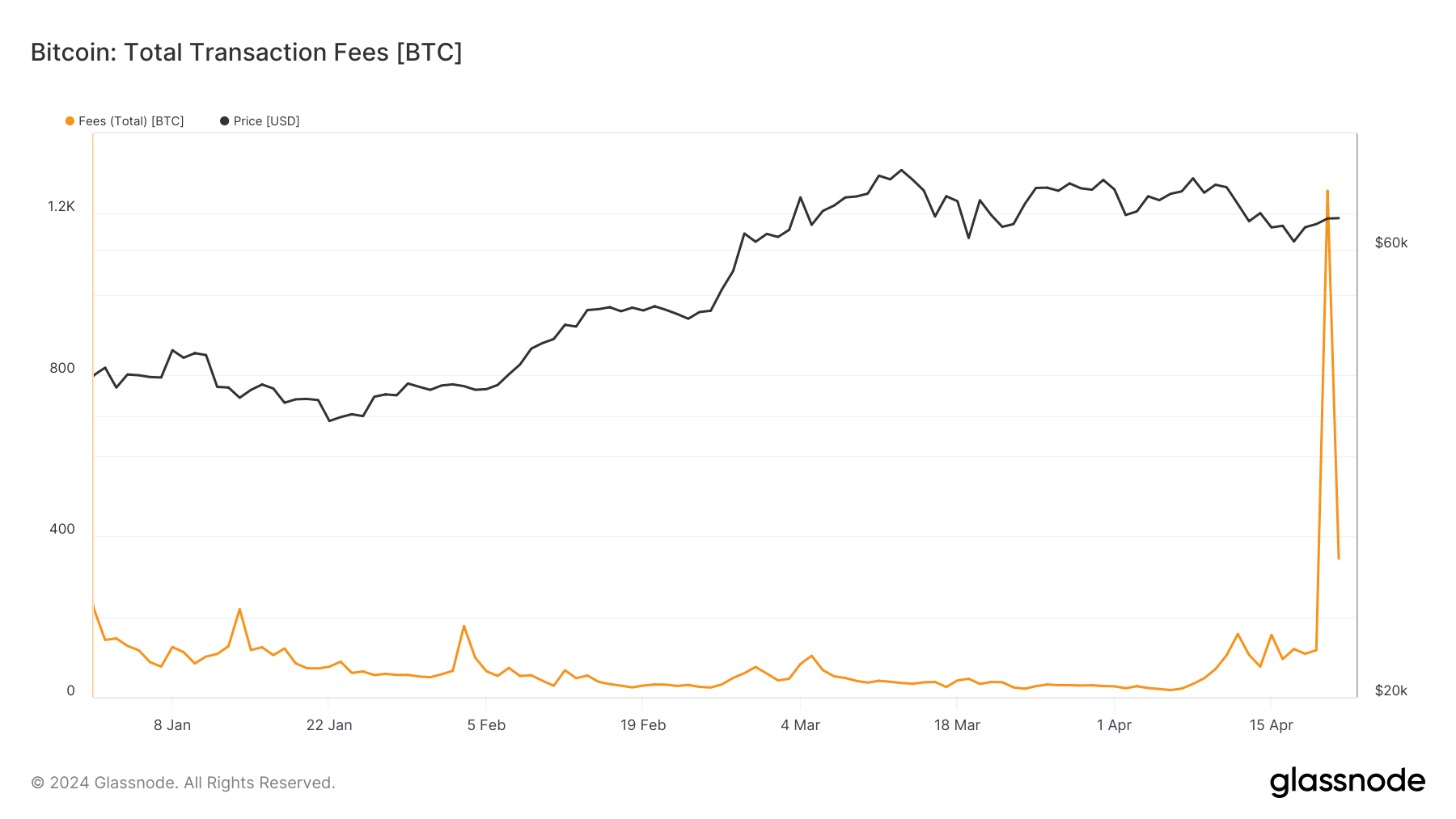
This demand for restricted block area drove transaction charges to historic highs, which paid 1,257 BTC to miners on the day of the halving. On April 19, the day earlier than the halving, the overall charges paid to miners had been 116 BTC, displaying simply how dramatic the escalation in transaction price was.
The next drop to 344 BTC in charges on April 21, whereas nonetheless considerably larger than pre-halving ranges, reveals the market normalized and commenced to regulate to the brand new mining economics.
The Price Ratio A number of (FRM) clearly reveals the impression of those heightened charges. The metric is used to guage the financial safety of a blockchain, notably because it transitions from block reward-based miner compensation to 1 predominated by transaction charges. The FRM is calculated by dividing the overall miner income, consisting of block rewards and transaction charges, with the transaction charges.
This metric helps assess how a lot of the mining revenue is derived from transaction charges quite than block rewards, providing insights into the blockchain’s sustainability as soon as block rewards are now not a major issue.
On April 19, the day earlier than the halving, the FRM stood at 9.01. It signifies that the overall miner income was roughly 9 occasions the quantity earned from transaction charges alone, with the vast majority of miner revenue nonetheless closely reliant on block rewards.
Because the block reward was decreased in half and the transaction charges elevated, the FRM dropped to 1.325, displaying simply how dramatic the shift in the direction of reliance on charges was. With the block reward decreased, transaction charges comprised a a lot bigger proportion of the overall miner income, lowering the FRM worth.
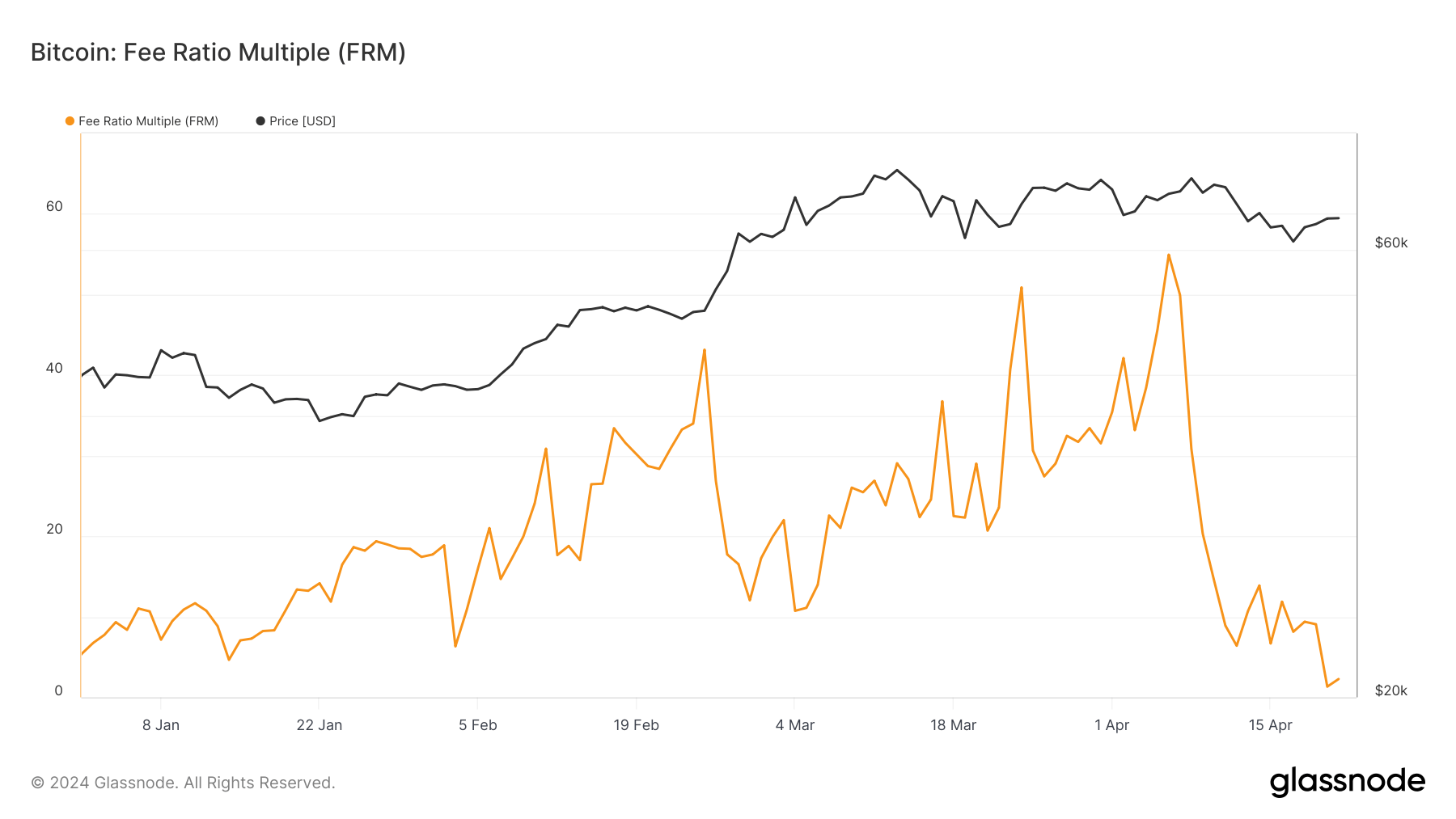
A decrease FRM worth implies that the blockchain is transferring nearer to a state the place it may theoretically maintain itself predominantly on transaction charges. That is essential for its long-term safety and viability as block rewards proceed to halve till they stop.
Nevertheless, this might negatively have an effect on a big a part of the community. As transaction charges start to represent a bigger portion of miner income, the associated fee to customers might improve, probably affecting how transactions are prioritized and impacting consumer conduct. This might result in even larger price spikes throughout peak demand.
The put up Bitcoin transaction charges surge to make up 75% of miner income post-halving appeared first on CryptoSlate.